Predicting Executive Function Impairments in Young Adults Using Machine Learning and Lifestyle Data
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17488/RMIB.47.1.1550Keywords:
cognitive impairments prediction, machine learning, neuropsychological testsAbstract
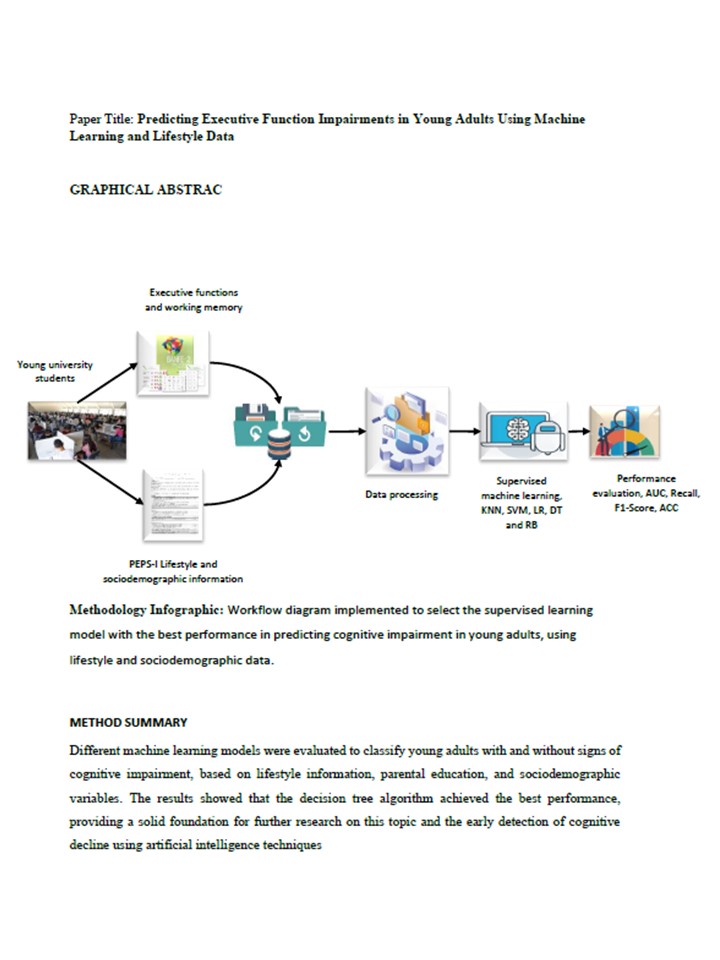
The development of executive function (EF) impairments in young individuals, such as difficulties with attention, memory, and problem-solving, is influenced by biological, social, and lifestyle factors. However, research on predicting these impairments remains limited due to a lack of reliable tools. This study analyzed 90 university students using EF tests, lifestyle, and sociodemographic questionnaires. Five machine learning models were evaluated: Decision Trees (DT), k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Support Vector Machines (SVM), Logistic Regression (LR), and Random Forest (RF), with cross-validation applied for model assessment. The results indicated a 62% incidence of EF impairments. Maternal education and nutrition were identified as key influencing factors. Among the models, DT performed best, achieving a recall of 61.9%, an F1-score of 62.1%, and an AUC of 66.54%, while RF had the lowest performance. Limitations include the cross-sectional nature of the data, which restricts causal inference, and the reliance on self-reported responses from participants, which may reduce data reliability. Despite these limitations, this study demonstrates the feasibility of using machine learning to predict EF impairments based on easily collected sociodemographic and lifestyle data. Sociodemographic and lifestyle variables are valuable predictors of EF impairments in young individuals. Machine learning tools offer a practical approach to assessing population-level EF health using accessible data.
Downloads
References
P. Anderson, “Assessment and development of executive function (ef) during childhood”, Child neuropsychology, vol. 8, no. 2, 2002, doi: https://doi.org/10.1076/chin.8.2.71.8724
J.R. Best and P.H. Miller, “A developmental perspective on executive function”, Child development, vol. 81, no. 6, 15 Nov. 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01499.x
A. Diamond, “Executive functions”, Annual review of psychology, vol. 64, no. 1, January 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750
C. Blair and C.C. Raver, “School readiness and self-regulation: A developmental psychobiological approach”, Annual review of psychology, vol. 66, no. 1, January 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010814-015221
S.J. Blakemore and S. Choudhury, “Development of the adolescent brain: implications for executive function and social cognition”, Journal of child psychology and psychiatry, vol. 47, no. 3-4, May 2006, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01611.x
A.G. Gutiérrez-García and M. Landeros-Velázquez, “Evaluación de funciones ejecutivas en estudiantes universitarios con niveles de autoeficacia percibida baja”, Revista Electrónica de Psicología Iztacala, vol. 20, no. 2, June 2017.
J. Flores, F. Ostrosky and A. Lozano,” Banfe-2 bateria neuropsicológica de funciones ejecutivas y lóbulos frontales. méxico: Manual moderno”, 2014.
F.S. Mogollón García, L.D. Becerra Rojas and J.S. Adolfo Ancajima Mauriola, “Estilos de vida saludables en estudiantes de pregrado”, Conrado, vol. 16, no. 75, July 2020. Available: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1990-86442020000400069&lng=es&tlng=es
Y.E. Salazar-Granizo, C. Hueso-Montoro and R.A. Caparros-Gonzalez, “Lifestyles and Academic Stress in University Students of Health Sciences: A Mixed-Methodology Study”, Healthcare, vol. 12, no. 1, January 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare12141384
J.R. Best, P.H. Miller and J.A. Naglieri, “Relations between executive function and academic achievement from ages 5 to 17 in a large, representative national sample”, Learning and individual differences, vol. 21, no. 4, August 2011, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2011.01.007
A. Diamond and D.S. Ling, “Conclusions about interventions, programs, and approaches for improving executive functions that appear justified and those that, despite much hype, do not”, Developmental cognitive neuroscience, vol. 18, no. 1, April 2016, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2015.11.005
N. Zhu, D.R. Jacobs, K. Meyer, K. He, L. Launer, J. Reis, K. Yaffe, S. Sidney, R. Whitmer and L. Steffen, “Cognitive function in a middle aged cohort is related to higher quality dietary pattern 5 and 25 years earlier: the cardia study”, The journal of nutrition, health & aging, vol. 19, no. 1, 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-014-0491-7
E.E. Bron, M. Smits, W.M. Van Der Flier, H. Vrenken, F. Barkhof, P. Scheltens, J.M. Papma, R.M. Steketee, C.M. Orellana, R. Meijboom, et al., “Standardized evaluation of algorithms for computer-aided diagnosis of dementia based on structural mri: the caddementia challenge”, NeuroImage, vol. 111, no. 1, 2015, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.01.048
C. Simfukwe, S.S. A. An and Y.C. Youn, “Comparison of machine learning algorithms for predicting cognitive impairment using neuropsychological tests”, Applied Neuropsychology: Adult, vol. 1, no. 1, Sep. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/23279095.2024.2392282
M.F. Jojoa-Acosta, S. Signo-Miguel, M.B. Garcia-Zapirain, M. Gimeno-Santos, A. Méndez-Zorrilla, C.J. Vaidya, M. Molins-Sauri, M. Guerra-Balic and O. Bruna-Rabassa, “Executive functioning in adults with down syndrome: machine-learning-based prediction of inhibitory capacity”, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 18, no. 20, sep. 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010785
K. Modi, I. Singh, Y. Kumar, “A comprehensive analysis of artificial intelligence techniques for the prediction and prognosis of lifestyle diseases”, Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, vol. 30, no. 8, june 2023, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-023-09957-2
L. Zhang, S. Zhao, W. Yang, Z. Yang, Z. Wu, H. Zheng, M. Lei, “Utilizing machine learning techniques to identify severe sleep disturbances in chinese adolescents: an analysis of lifestyle, physical activity, and psychological factors”, Frontiers in Psychiatry, vol. 15, nov. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1447281
Z. John Lu, “The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction”, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series A: Statistics in Society, vol. 173, no. 3, june 2010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-985X.2010.00646_6.x
S. Gornale, S. Kumar, R. Siddalingappa, P.S, “ Hiremath, Survey on handwritten signature biometric data analysis for assessment of neurological disorder using machine learning techniques”, Transactions on Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence, vol. 10, no. 2, April 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.14738/tmlai.102.12210
S. Swati, M. Kumar, S. Namasudra, “Early prediction of cognitive impairments using physiological signal for enhanced socioeconomic status”, Information Processing & Management, vol. 59, no. 2, March 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2021.102845
J. Hou, H. Jiang, Y. Han, R. Huang, X. Gao, W. Feng, Z. Guo, “Lifestyle influence on mild cognitive impairment progression: A decision tree prediction model study”, Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, vol. 20, no. 1, Feb. 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S435464
D.W. Hosmer Jr, S. Lemeshow, R.X, Sturdivant, Applied logistic regression, 3rd ed. USA: John Wiley & Sons, pp. 35.
L. Breiman, “Random forests”, Machine learning, vol. 45, no. 1, Jan. 2001, doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
D.M. Powers, “Evaluation: from precision, recall and f-measure to roc, informedness, markedness and correlation”, International Journal of Machine Learning Technology, vol 2, no. 1, Jan. 2001, doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2010.16061
G.W. Evans, P. Kim, “Childhood poverty, chronic stress, self-regulation, and coping”, Child development perspectives, vol. 7, no. 1, Nov. 2013, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/cdep.12013
P.E. Davis-Kean, “The influence of parent education and family income on child achievement: the indirect role of parental expectations and the home environment”, Journal of family psychology, vol. 19, no. 2, Sep. 2005, doi: https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-3200.19.2.294
P. Glewwe, E.A. Miguel, “The impact of child health and nutrition on education in less developed countries” Handbook of development economics, vol. 4, 2007, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1573-4471(07)04056-9
UNESCO, Global Education Monitoring Report 2019: Migration, Displacement and Education-Building Bridges, Not Walls ,UN, Mexico, 2018. Accessed: Feb. 25, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12799/6023
K.Y.C. Cuellar, G.I. Díaz, R.A. Ortíz, N.M. Pérez, J.G. Ariza, “Genealogías culturales e historias de familia en oaxaca: Diseño epistémico, estrategia metodológica y reflexividad”, Estudios sobre las culturas contemporáneas, vol. 20, no. 40, 2014. Accessed: Dec. 12, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=4990957
J.R. Ocaña-Noriega, G.S. Sagñay-Llinin, “La malnutrición y su relación en el desarrollo cognitivo en niños de la primera infancia”, Polo del conocimiento, vol. 5, No. 12, Sep. 2020, doi: https://doi.org/0000-0002-7819-9115
J.A. Cardona Murillo, F.Z. Leidy Andrea, “Influencia de la alimentación en el desarrollo cognitivo de los estudiantes en el grado de transición de la institución educativa Luis Carlos Galán Sarmiento del municipio de Carepa”, Corporación Universitaria Minuto de Dios, Urabá, Antioquia, Colombia, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://repository.uniminuto.edu/items/9c2b881d-8efc-4eee-941b-3901a995d529
J. Bernal, “Resiliencia, infancia y nutrición: propuesta de indicadores para medición en niños y adolescentes”, Revista Salud Bosque, vol. 7, no. 2, Feb. 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.18270/rsb.v7i2.2192
P. Zaninotto, G.D. Batty, M. Allerhand, I.J. Deary, “Cognitive function trajectories and their determinants in older people: 8 years of follow-up in the English longitudinal study of ageing”, J Epidemiol Community Health, vol. 72, no. 8, Aug. 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2017-210116
G.R. Poudel, A. Barnett, M. Akram, E. Martino, L.D. Knibbs, K.J. Anstey, J.E. Shaw, E. Cerin, “Machine learning for prediction of cognitive health in adults using sociodemographic, neighbourhood environmental, and lifestyle factors”, Inter- national Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 19, no. 17, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710977
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Revista Mexicana de Ingenieria Biomedica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Upon acceptance of an article in the RMIB, corresponding authors will be asked to fulfill and sign the copyright and the journal publishing agreement, which will allow the RMIB authorization to publish this document in any media without limitations and without any cost. Authors may reuse parts of the paper in other documents and reproduce part or all of it for their personal use as long as a bibliographic reference is made to the RMIB. However written permission of the Publisher is required for resale or distribution outside the corresponding author institution and for all other derivative works, including compilations and translations.







